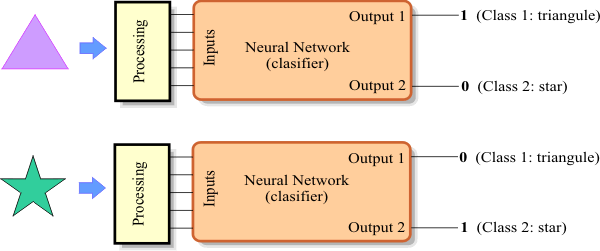
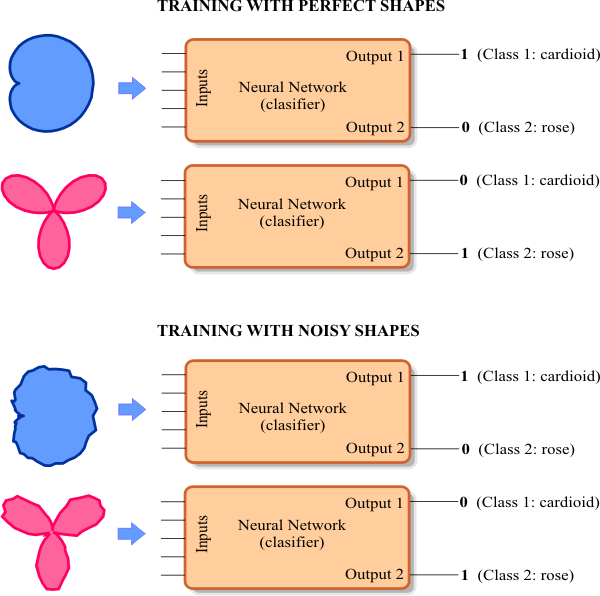
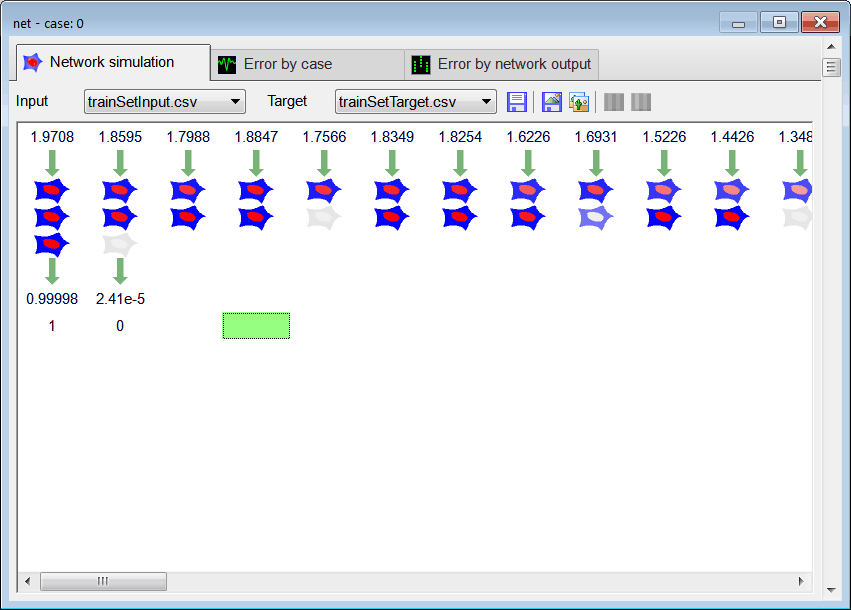
//_________________________ Network Setup
LayerNet net;
net.Create(64, 12, 0, 2);
int i = 0;
//____________________________ Input Scaling
for(i = 0; i<64; i++)
{
net.SetInScaler(i, 0, 2); // Input values are from 0 to 2
}
//____________________________ Output Scaling
for(i = 0; i<2; i++)
{
net.SetOutScaler(i, 0.0, 1.0); // Output values are from 0 to 1
}
//________________________ Load and set the training set
Matrix trainSetInput;
trainSetInput.Load();
Matrix trainSetTarget;
trainSetTarget.Load();
net.SetTrainSet(trainSetInput, trainSetTarget, false);
//________________________ Train
net.TrainSimAnneal(10, 20, 15, 0.01, false, 4, 1.0e-12);
net.TrainConjGrad(2500,1.0e-12);
//_____________________________ Save the trained network
net.Save();
|
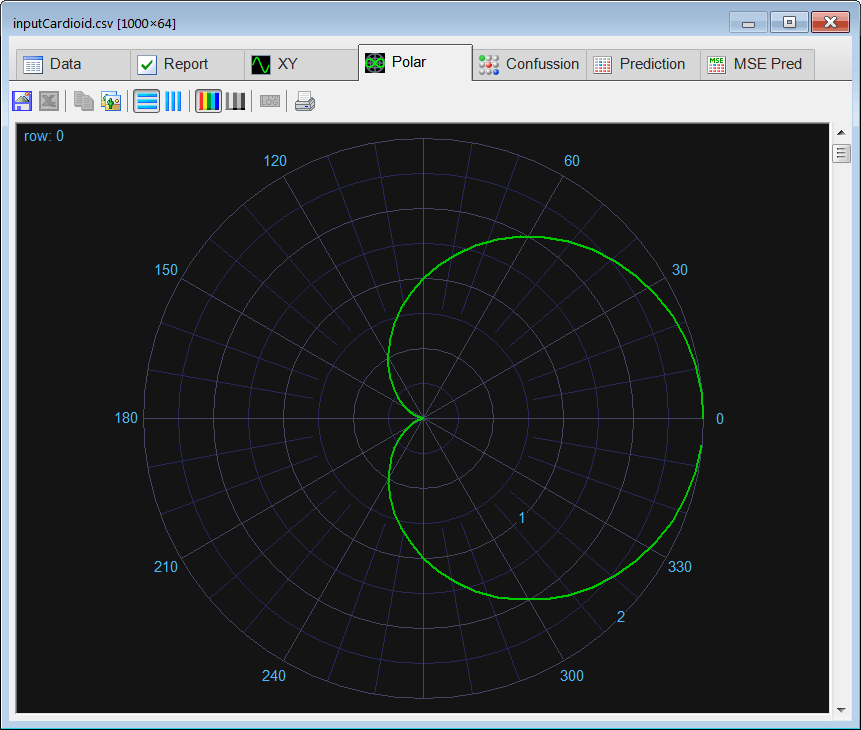
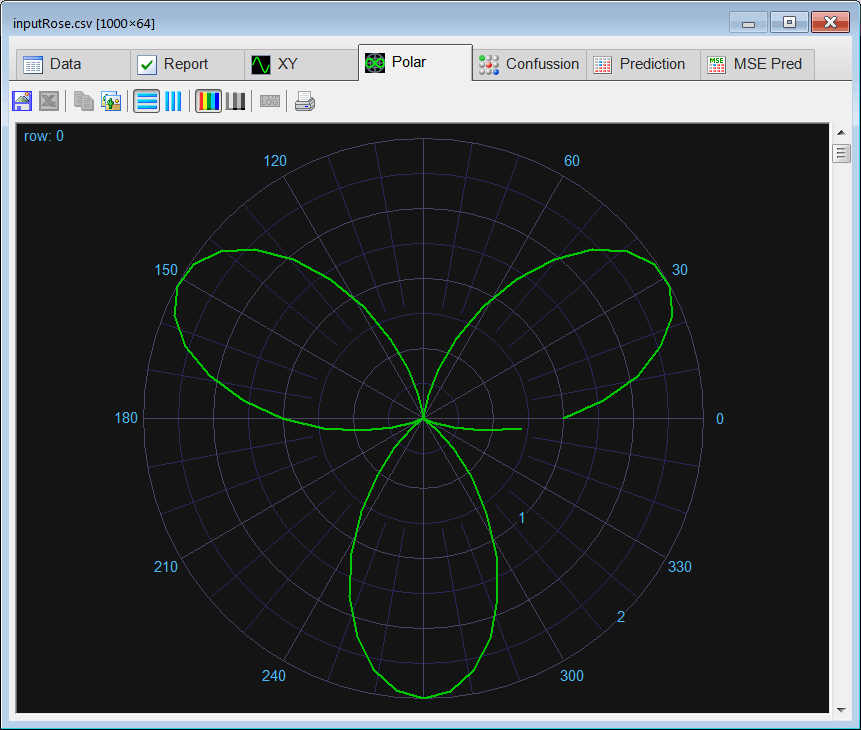
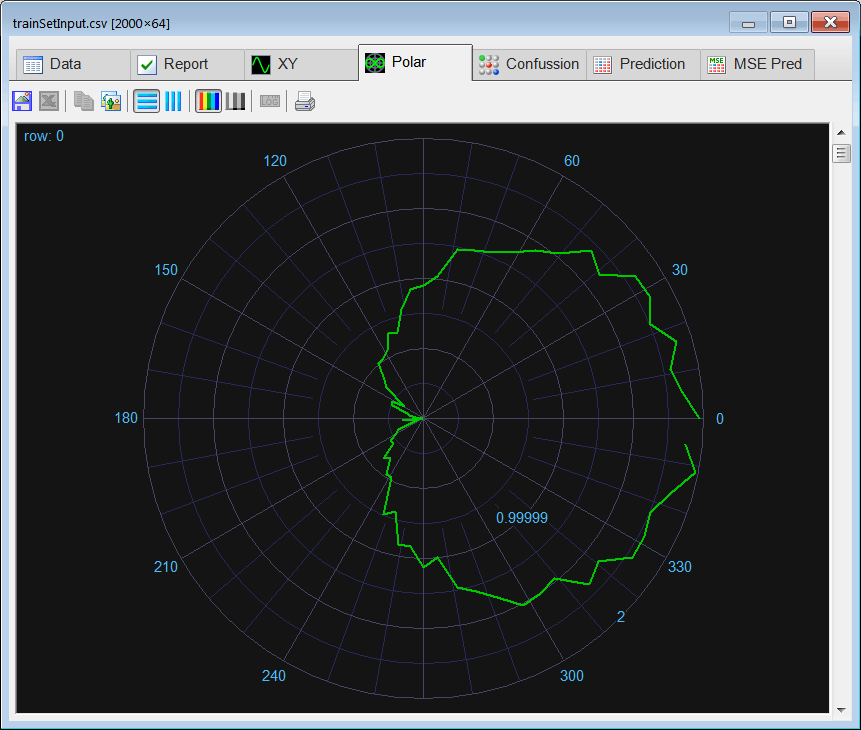
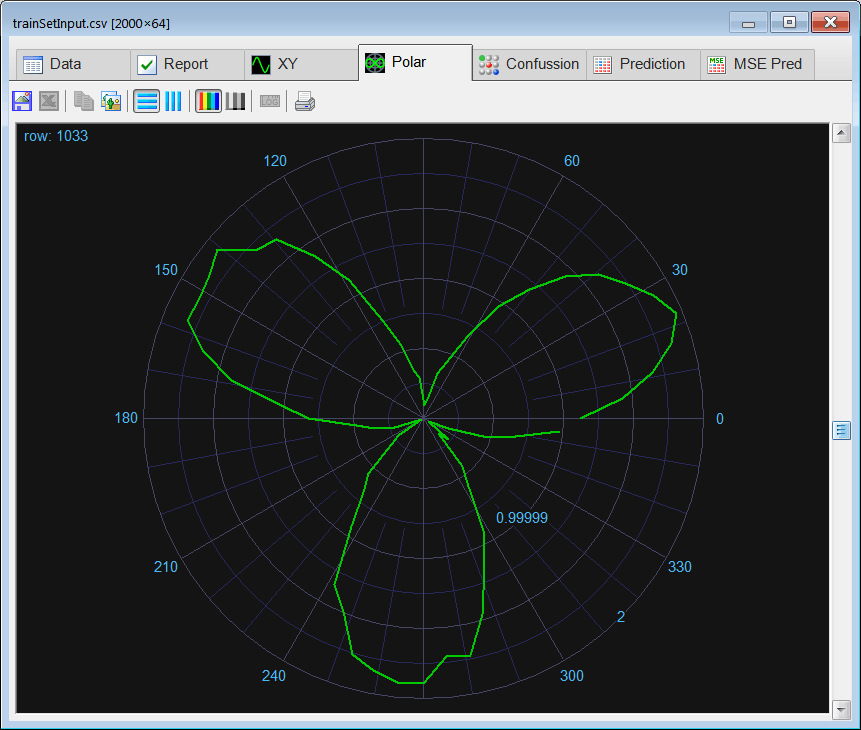
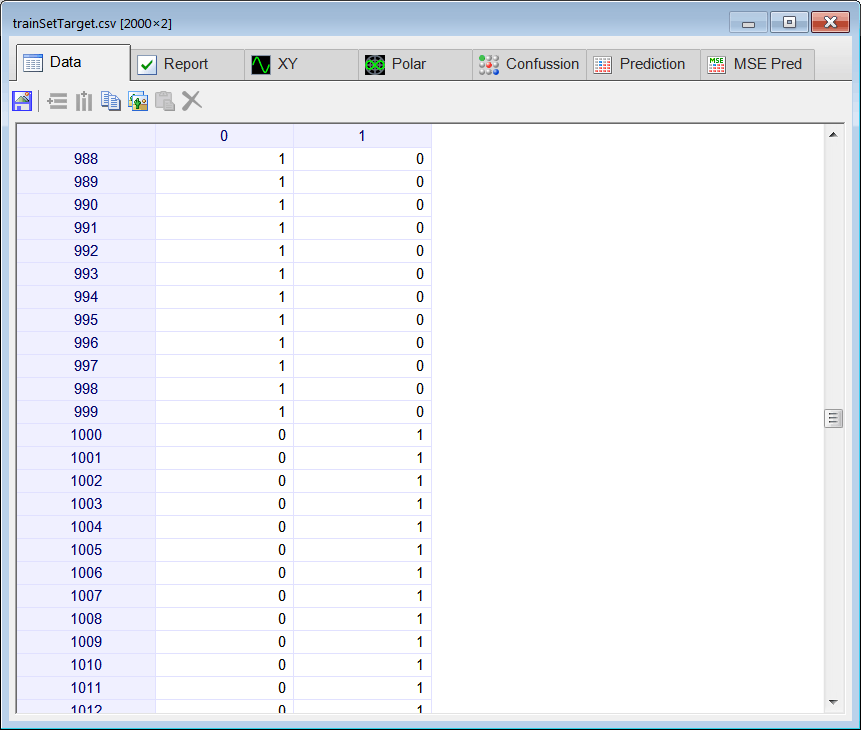
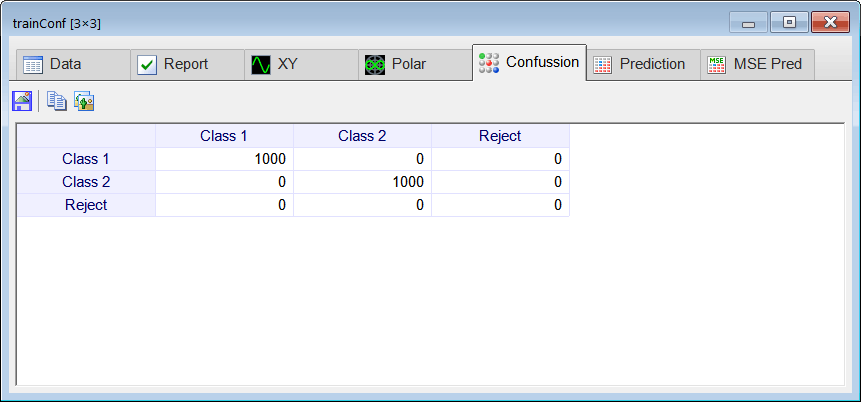
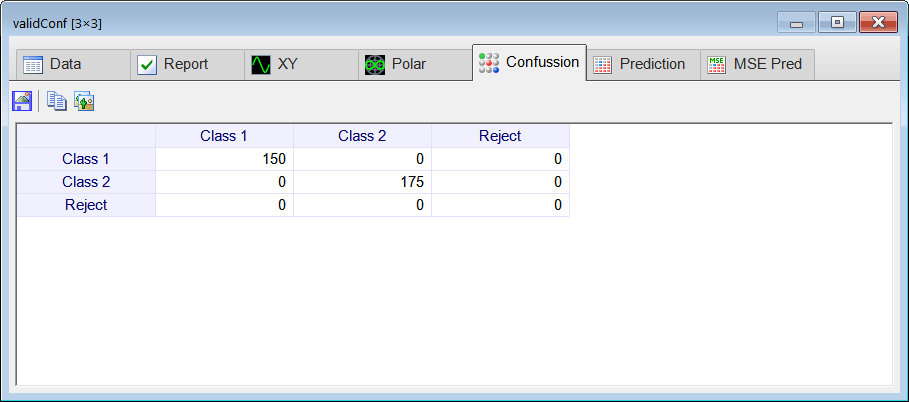
 Runclick the button to execute the code. If you do not have any errors, the training set will be generated and displayed on the variable list and the file list. Click on the file to see its contents. The first 1000 rows of the training set are the Cardioid shape; the second 1000 rows of the training set are the Rose shape. The training set target has two columns, the first column is for class 1 (Cardioid) and the second column is for class 2 (Rose).
Runclick the button to execute the code. If you do not have any errors, the training set will be generated and displayed on the variable list and the file list. Click on the file to see its contents. The first 1000 rows of the training set are the Cardioid shape; the second 1000 rows of the training set are the Rose shape. The training set target has two columns, the first column is for class 1 (Cardioid) and the second column is for class 2 (Rose).